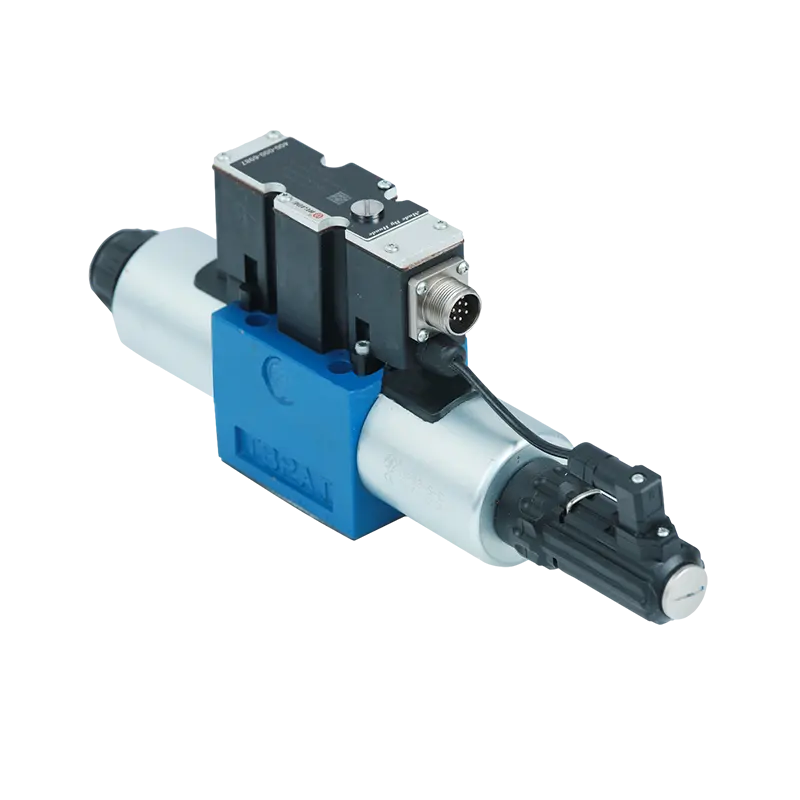
Imagine you're conducting an orchestra. You don't just tell musicians to play "loud" or "quiet" - you give them subtle hand gestures that say "a little softer," "gradually louder," or "hold that exact volume." A hydraulic proportional valve is like a conductor for hydraulic fluid, providing infinitely variable control instead of just "on" or "off."
A hydraulic proportional valve is an electro-hydraulic control device that converts electrical signals into precise hydraulic flow, pressure, or directional control. Unlike traditional valves that are either fully open or fully closed, proportional valves can maintain any position between these extremes, providing smooth, accurate control.
For basics, start with what is a proportional valve.
How Do Hydraulic Proportional Valves Work?
Let's follow the journey of control from an electrical signal to precise hydraulic action.
[See detailed explanation of how proportional valves work.]
Real-World Example: When an excavator operator moves their joystick halfway, the proportional valve receives a 50% signal. The spool moves to a position that allows exactly half the maximum flow to the hydraulic cylinder, resulting in smooth, controlled arm movement at exactly half speed.
Proportional Valve vs Servo Valve vs On/Off Valve
Understanding the differences between valve types is crucial for making the right choice:
| Feature | On/Off Valve | Proportional Valve | Servo Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Binary (Open/Closed) | Infinite positioning | Ultra-precise positioning |
| Response Time | 10-100 ms | 5-50 ms | 1-10 ms |
| Accuracy | ±5-10% | ±1-3% | ±0.1-0.5% |
| Cost | $50-500 | $500-5,000 | $2,000-20,000 |
| Energy Efficiency | Poor | Good | Excellent |
- Choose On/Off Valves when: Simple start/stop control is sufficient, budget is extremely tight, or environment is dirty.
- Choose Proportional Valves when: You need variable speed/pressure control, energy efficiency matters, and smooth operation is important.
- Choose Servo Valves when: Ultra-high precision is critical, very fast response is needed, and budget allows for premium performance.
Types of Hydraulic Proportional Valves
By Function: The Three Main Categories

1. Proportional Directional Control Valves
What they do: Control both direction and speed of hydraulic actuators.
Think of it as: A smart traffic controller that not only directs traffic but also controls speed limits.
Best for: Machine tools, injection molding, general automation.

What they do: Maintain precise system pressure regardless of flow demands.
Think of it as: A smart water pressure regulator that keeps shower pressure perfect even when someone turns on the dishwasher.
Best for: Press operations, clamping systems, pressure testing.

What they do: Maintain exact flow rates independent of pressure changes.
Think of it as: A cruise control system for hydraulic flow.
Best for: Speed control, synchronized operations, metering applications.
By Construction: Understanding the Mechanics
-
Direct-Acting Proportional Valves: Electromagnet directly moves the main spool. Simpler construction, lower cost. Perfect for mid-size applications (up to 100 GPM).

- Pilot-Operated Proportional Valves: Small pilot valve controls main valve operation. Higher flow (500+ GPM) and pressure capabilities. Perfect for large industrial systems.

Performance Characteristics That Matter
The heart of proportional valve performance lies in how accurately it converts electrical signals to hydraulic output.
- Linearity (±0.5% to ±3%): Imagine drawing a straight line on graph paper. Linearity measures how close your valve's actual performance comes to that perfect straight line.
- Hysteresis (±0.5% to ±5%): This measures the difference in output when you approach the same setpoint from different directions. Less hysteresis means more precise control.
- Repeatability (±0.1% to ±2%): How consistently does the valve perform the same operation? Better repeatability means more reliable performance.
- Response Time (5-100 milliseconds): How quickly does the valve respond to signal changes? Faster response prevents system instability.
The fundamental flow equation is:
Q = Cd × A × √(2ΔP/ρ)This equation shows why proportional valves are so effective: by precisely controlling the area (A), they provide accurate flow control (Q) regardless of pressure variations.
Real-World Success Stories
Case Study 1: The Injection Molding Revolution
The Solution: Implementing Moog D941 proportional valves for injection speed and pressure control.
Case Study 2: Mobile Equipment Precision
The Solution: Danfoss PVG 48 proportional valve system with electronic joysticks replaced binary controls.
Case Study 3: Steel Mill Precision
The Solution: ATOS DPZO proportional pressure valves with integrated feedback control for rolling mills.
Selection Guide
Step 1: Define Your System Requirements
Before browsing catalogs, determine these key specifications:
- Maximum system pressure (PSI)
- Required flow rate (GPM)
- Operating temperature range
- Response time and Accuracy requirements
- Control signal type (Voltage / Current / Digital)
Step 2: Application-Specific Considerations
- Manufacturing: Look for valves with integrated electronics and fieldbus communication capabilities.
- Mobile Equipment: Choose valves rated for vibration/shock and evaluate power consumption.
- Aerospace: Select valves with redundant feedback systems and special materials.
Step 3: Brand Overview
Bosch Rexroth ($1,500-8,000): Best for industrial automation and factory equipment. Strong Industry 4.0 integration.
Parker Hannifin ($2,000-12,000): Best for high-performance applications and aerospace. Known for voice coil technology.